The Federal Reserve interest rates play a pivotal role in shaping the U.S. economy and influencing global financial markets. These rates are a critical tool used by the Federal Reserve to manage inflation, unemployment, and overall economic stability. As one of the most important monetary policy instruments, understanding federal reserve interest rates is essential for anyone interested in economics, investing, or personal finance.
Interest rates set by the Federal Reserve, commonly referred to as the federal funds rate, have far-reaching effects. They impact borrowing costs for consumers and businesses, influence stock and bond markets, and affect currency values. Whether you're a homeowner considering a mortgage, an investor looking to allocate capital, or a business owner planning for the future, federal reserve interest rates are a key factor to consider.
This article will delve into the intricacies of federal reserve interest rates, exploring their purpose, how they are determined, and their impact on various sectors of the economy. By the end of this guide, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of why these rates matter and how they can affect your financial decisions.
Read also:Exploring The Life And Achievements Of Lee Sunkyun A Journey Through Talent And Dedication
Table of Contents
- What Are Federal Reserve Interest Rates?
- The Role of the Federal Reserve
- How Are Federal Reserve Interest Rates Determined?
- Effects on the Economy
- Federal Reserve Interest Rates and the Stock Market
- Historical Trends
- Federal Reserve Interest Rates and Global Markets
- Tools Used by the Federal Reserve
- Future Outlook
- Conclusion
What Are Federal Reserve Interest Rates?
Federal Reserve interest rates refer to the target range for the federal funds rate, which is the interest rate at which banks lend reserve balances to other banks on an overnight basis. This rate is set by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), a branch of the Federal Reserve System. The federal funds rate serves as a benchmark for other interest rates, such as those for mortgages, credit cards, and auto loans.
The federal funds rate is a crucial monetary policy tool used to influence economic conditions. By adjusting this rate, the Federal Reserve can encourage or discourage borrowing and spending, thereby affecting economic growth. For example, lowering the federal funds rate typically makes borrowing cheaper, stimulating economic activity, while raising it can help control inflation by reducing spending.
Understanding federal reserve interest rates requires recognizing their dual mandate: promoting maximum employment and stable prices. These goals guide the Federal Reserve's decisions regarding interest rate adjustments.
The Role of the Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve, often referred to as the "Fed," is the central banking system of the United States. Its primary responsibilities include conducting monetary policy, supervising and regulating banks, maintaining the stability of the financial system, and providing financial services to the U.S. government.
One of the key functions of the Federal Reserve is managing monetary policy through the use of federal reserve interest rates. By adjusting these rates, the Fed aims to achieve its dual mandate of maximum employment and price stability. This involves balancing economic growth with inflation control, ensuring that the economy remains healthy without overheating.
The Federal Reserve also plays a critical role in times of financial crisis, acting as a lender of last resort to stabilize the financial system. Its actions during such periods can have significant impacts on global markets, making it one of the most influential financial institutions in the world.
Read also:Paul Wall The Southern Rap Icon And Entrepreneurial Pioneer
How Are Federal Reserve Interest Rates Determined?
Federal Reserve interest rates are determined by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), which meets eight times a year to assess economic conditions and set monetary policy. During these meetings, FOMC members review a wide range of economic data, including inflation rates, employment figures, and GDP growth.
The decision to raise, lower, or maintain the federal funds rate is based on the FOMC's assessment of current and future economic conditions. Factors such as inflationary pressures, labor market conditions, and global economic developments are carefully considered. The goal is to set a rate that promotes economic growth while keeping inflation in check.
In addition to the federal funds rate, the FOMC also sets a target range for interest rates, providing flexibility to respond to changing economic conditions. This approach allows the Federal Reserve to make adjustments as needed to achieve its policy objectives.
Effects on the Economy
Inflation and Unemployment
Federal reserve interest rates have a direct impact on inflation and unemployment, two key indicators of economic health. By adjusting these rates, the Federal Reserve can influence the overall level of economic activity, affecting both inflation and employment levels.
For example, when inflation is too high, the Fed may raise interest rates to reduce spending and borrowing, thereby slowing down economic growth and bringing inflation under control. Conversely, during periods of high unemployment, the Fed may lower interest rates to encourage borrowing and spending, stimulating job creation and economic expansion.
This balancing act is critical for maintaining economic stability and ensuring that the economy remains on a sustainable growth path. The Federal Reserve's ability to manage these variables effectively is a testament to its importance in the financial system.
Consumer Spending and Saving
Consumer behavior is significantly influenced by federal reserve interest rates. Lower interest rates make borrowing more affordable, encouraging consumers to spend more on big-ticket items like homes, cars, and appliances. This increased spending can boost economic growth and create jobs.
On the other hand, higher interest rates make saving more attractive, as consumers earn higher returns on savings accounts and certificates of deposit. This can lead to increased savings and reduced spending, potentially slowing economic growth. The interplay between spending and saving is a key factor in the Federal Reserve's decision-making process.
Federal Reserve Interest Rates and the Stock Market
The relationship between federal reserve interest rates and the stock market is complex and dynamic. Changes in interest rates can have both direct and indirect effects on stock prices, influencing investor sentiment and market performance.
Lower interest rates tend to be positive for the stock market, as they reduce borrowing costs for companies and consumers alike. This can lead to increased corporate profits and higher stock prices. Conversely, higher interest rates can weigh on the stock market, as they increase borrowing costs and reduce consumer spending, potentially leading to lower corporate earnings and stock price declines.
Investors closely monitor Federal Reserve announcements and economic data to anticipate changes in interest rates and adjust their portfolios accordingly. The Fed's communication strategy, often referred to as "forward guidance," plays a crucial role in shaping market expectations and influencing investment decisions.
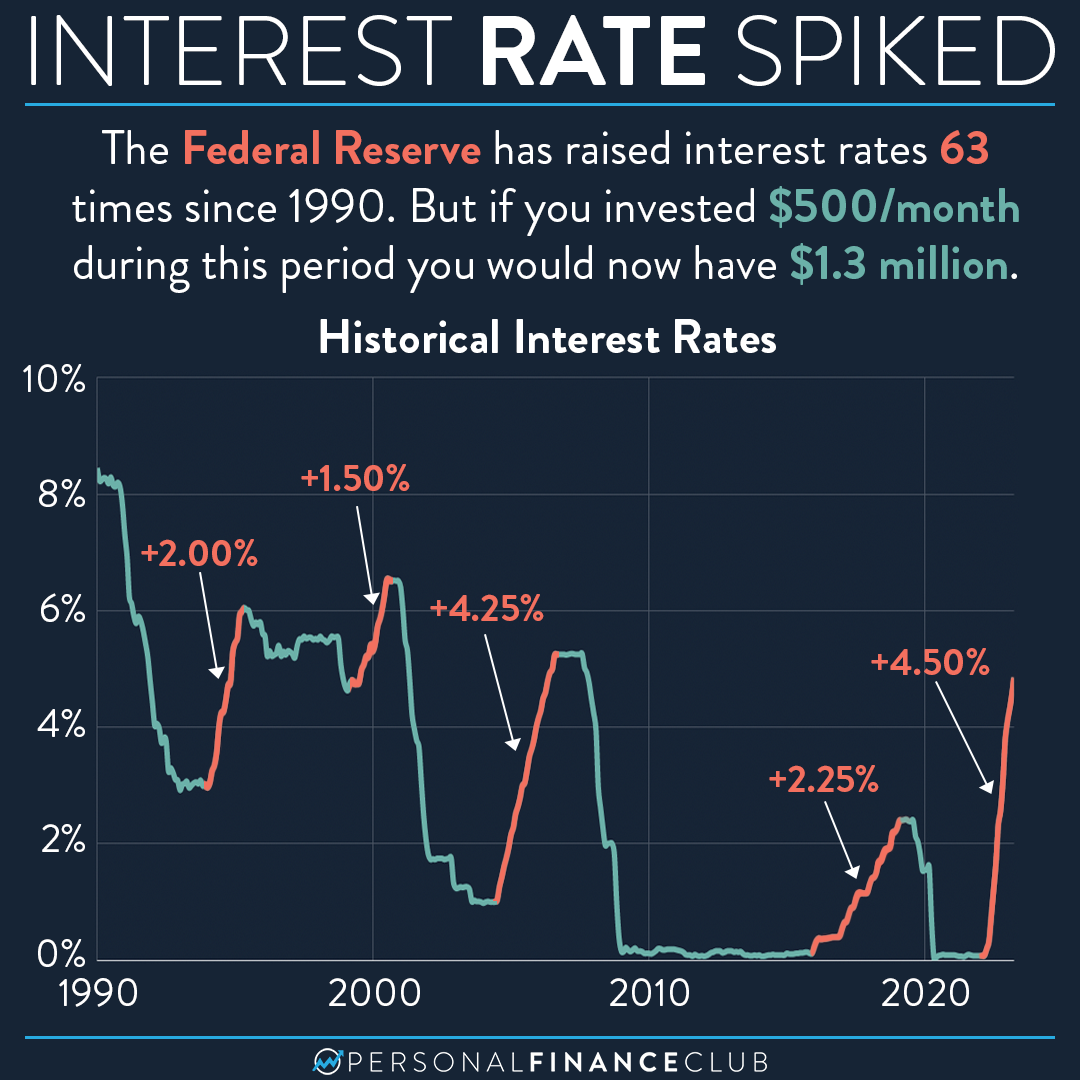
Historical Trends
Throughout history, federal reserve interest rates have fluctuated in response to changing economic conditions. During periods of rapid economic growth, the Fed has often raised rates to prevent overheating and control inflation. Conversely, during economic downturns, the Fed has lowered rates to stimulate recovery.
One notable example is the 2008 financial crisis, during which the Federal Reserve lowered interest rates to near zero to stabilize the financial system and promote economic recovery. This period of ultra-low rates lasted for several years, helping to support the housing market and encourage borrowing and spending.
More recently, the Fed has begun gradually increasing interest rates as the economy has strengthened, reflecting its confidence in the sustainability of economic growth. These historical trends highlight the Federal Reserve's role in navigating economic cycles and maintaining stability.
Federal Reserve Interest Rates and Global Markets
Federal reserve interest rates have far-reaching effects on global financial markets. As the world's largest economy, the United States plays a central role in the global financial system, and changes in U.S. interest rates can ripple through markets worldwide.
For example, higher U.S. interest rates can attract foreign capital, strengthening the dollar and affecting currency exchange rates. This can impact trade balances and influence economic conditions in other countries. Additionally, changes in U.S. interest rates can affect global bond and stock markets, influencing investment flows and asset prices.
The interconnectedness of global markets means that the Federal Reserve's decisions regarding interest rates are closely watched by investors and policymakers around the world. Its actions can have significant implications for international trade, investment, and economic stability.
Tools Used by the Federal Reserve
In addition to setting federal reserve interest rates, the Federal Reserve employs a range of tools to implement monetary policy and maintain economic stability. These tools include open market operations, reserve requirements, and forward guidance.
Open market operations involve the buying and selling of government securities to influence the money supply and interest rates. Reserve requirements dictate the amount of funds banks must hold in reserve, affecting their ability to lend. Forward guidance provides information about the Fed's future policy intentions, helping to shape market expectations and influence economic behavior.
These tools, along with federal reserve interest rates, form the foundation of the Federal Reserve's monetary policy framework, enabling it to effectively manage economic conditions and promote stability.
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, the Federal Reserve faces several challenges in managing federal reserve interest rates and maintaining economic stability. These include navigating the complexities of a rapidly changing global economy, addressing the impacts of technological advancements, and adapting to shifting demographic trends.
As the U.S. economy continues to evolve, the Federal Reserve must remain agile and responsive, adjusting its policies as needed to achieve its dual mandate. This requires a deep understanding of economic data and a commitment to transparency and communication with the public and financial markets.
The future of federal reserve interest rates will depend on a variety of factors, including inflation trends, employment levels, and global economic conditions. By staying informed and proactive, the Federal Reserve can continue to play a vital role in promoting economic growth and stability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, federal reserve interest rates are a critical component of the U.S. economy, influencing everything from inflation and unemployment to consumer behavior and global markets. Understanding these rates and their impact is essential for anyone seeking to navigate the complexities of modern finance.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and insights in the comments section below. Are there specific aspects of federal reserve interest rates you'd like to explore further? Let us know, and don't forget to check out our other articles for more in-depth analysis of economic and financial topics. Together, we can deepen our understanding of the forces shaping our world and make informed decisions for the future.
Data sources and references: